You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Example 1:
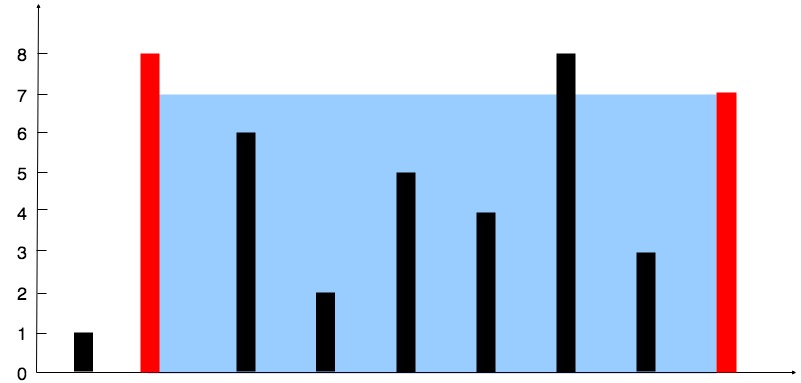
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2:
Input: height = [1,1]
Output: 1Constraints:
n == height.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= height[i] <= 104
SOLUTION:
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
maxA: int=0
l: int=0
r: int=len(height)-1
while l < r:
h: int=min(height[l], height[r])
maxA = max(maxA, (h * (r-l)))
if h==height[l]:
l =l+1
else:
r =r-1
return maxA
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity:O(1)
How it works:
This code uses a two-pointer approach to find the container with the maximum area.
- Initialize
maxAto 0, which will hold the maximum area. - Initialize
lto 0, representing the left pointer, andrtolen(height) - 1, representing the right pointer. - Enter a
whileloop, which runs as long aslis less thanr. - Calculate the height
has the minimum value betweenheight[l]andheight[r]. - Calculate the area
h * (r - l)and updatemaxAif this area is greater than the current maximum area. - Move the pointers inward based on the height comparison.
- If
his equal toheight[l], incrementlby 1. - If
his equal toheight[r], decrementrby 1.
- If
- After the
whileloop ends, return the maximum areamaxA.
Comments
Post a Comment