Given an array of integers heights representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
Example 1:
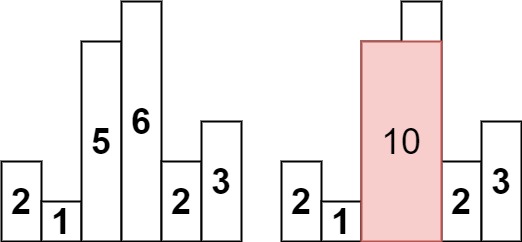
Input: heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
Output: 10
Explanation: The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1.
The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.
Example 2:
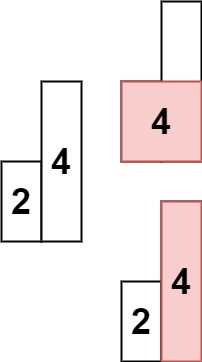
Input: heights = [2,4]
Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= heights.length <= 1050 <= heights[i] <= 104
Time Complexity: O(n) ->The for loop iterates over the list heights once. The while loop iterates over the stack at most once for each bar. Therefore, the total time complexity of the code is O(n).
Space Complexity: O(n) -> The stack can store at most n elements, where n is the number of bars in the histogram. Therefore, the space complexity of the code is O(n).
How it works:
- The
forloop iterates over the listheights. For each iteration, the current bar is stored in the variableh. - The variable
startis initialized to the current indexi. - The
whileloop checks if the stack is not empty and the top bar on the stack is taller than the current bar. If it is, we pop the top bar off the stack and update the variablestartto the index of the popped bar. - The
stack.append((start, h))line appends the current indexiand the current barhto the stack. - The
forloop iterates over the stack. For each iteration, the current index and height are stored in the variablesiandh. - The
maxarea = max(maxarea, h * (len(heights)-i) )line calculates the area of the rectangle formed by the current bar and the bars that are stacked below it. - The
return maxarealine returns the maximum area found.
The algorithm works by maintaining a stack of indices of the bars that form the top of the largest rectangle. The stack is initialized with the index of the first bar. For each subsequent bar, we check if it is taller than the top bar on the stack. If it is, we pop the top bar off the stack and add the new bar to the stack. We continue this process until we reach the end of the list.
Once we have processed all of the bars, we can calculate the area of the largest rectangle by multiplying the height of the top bar on the stack by the width of the rectangle. The width of the rectangle is the number of bars that are stacked below the top bar.

Comments
Post a Comment