A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node's values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
Example 1:
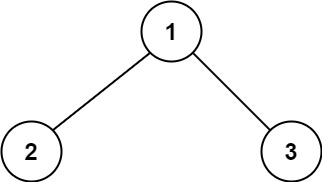
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 6
Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
Example 2:
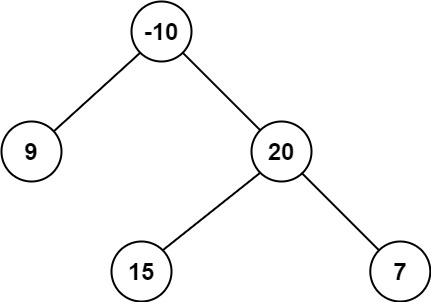
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 42
Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3 * 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
SOLUTION
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity:O(n)
How it works:
The
maxPathSummethod takes arootnode of a binary tree as input and returns an integer, which represents the maximum path sum.Inside the
maxPathSummethod, a variableresultis initialized as a list with a single element, which is the value of therootnode. This list is used to keep track of the maximum path sum throughout the recursion.The code defines a nested function
dfs(depth first search) that performs a recursive depth-first traversal of the binary tree.The
dfsfunction takes arootnode as input and returns an integer representing the maximum path sum starting from the current node.Inside the
dfsfunction, it first checks if therootnode isNone. If it isNone, it means we have reached the end of a branch, so the function returns 0.If the
rootnode is notNone, the function recursively calls itself on the left and right child nodes of the current node and assigns the returned values tomaxLeftandmaxRightvariables, respectively.After getting the maximum path sums from the left and right subtrees, the code checks if they are negative (less than 0) and assigns them a value of 0. This step is done to exclude negative contributions from the maximum path sum.
The code then calculates the maximum path sum by adding the value of the current node,
root.val, to the maximum ofmaxLeftandmaxRight.Next, the code updates the
resultlist by taking the maximum between the current maximum path sum (result[0]) and the maximum path sum that includes the current node (root.val + maxLeft + maxRight).Finally, the
dfsfunction returns the maximum path sum starting from the current node, which is the sum of the current node's value and the maximum ofmaxLeftandmaxRight.Outside the
dfsfunction, themaxPathSummethod calls thedfsfunction with therootnode to start the recursion.Finally, the
maxPathSummethod returns the maximum path sum stored in theresultlist.
In summary, this code uses a depth-first search approach to recursively calculate the maximum path sum in a binary tree. It keeps track of the maximum path sum encountered so far in the result list, which is updated during the traversal.
Comments
Post a Comment